Microfabrication
The microfabrication and soft-lithographic capabilities of our NBE facilities are aimed at thin and thick film (screen-printed) biosensors, printable electronic devices, micro total analysis systems (µ-TAS), polymeric and glass micro separation devices and screen-printed electrodes using the following equipment:
- UV Exposure System
- High resolution, cutting-edge 3D printer.
- High-precision semi-automatic screen printer (Model TF 100, MPM- Speedline Inc)
- Nikon video microscopes
- CAD graphic work stations
- Viscometer, centrifugal mixer
- Tension/compression test stand (stretch stage with digital force gauge)
- Photonic sintering
Printed electronics offers many new applications in diverse fields such as sensor arrays and energy harvesting devices. Printed electronics involves development of new materials in connection to various fabrication processes. Our expertise in printed and flexible electronics can be applied to a broad range of applications.
PLEASE CONTACT US FOR YOUR OWN SCREEN PRINTING SENSOR NEEDS.
Recent Publications:
“Built‐In Active Microneedle Patch with Enhanced Autonomous Drug Delivery”, M. A. Lopez‐Ramirez, F. Soto, et al, Adv. Mater., 1905740 (2019); DOI: 10.1002/adma.201905740.
“Highly Stretchable Fully-Printed CNT-based Electrochemical Sensors and Biofuel Cells: Combining Intrinsic and Design-induced Stretchability” A. J. Bandodkar, I. Jeerapan, J.-M. You, R. Nuñez-Flores, J. Wang, Nano Letters, 16 (2016) 721–727.
“All Printed Stretchable Electrochemical Devices”, Banodkar et al, Advanced Materials, 27 (2015) 3060.
“Nanomotor Lithography”, J. Li, et al, Nature Communications 5 (2014) 5026.
“From All-Printed 2D Patterns to Free-Standing 3D Structures: Controlled Buckling and Selective Bonding”, L Yin et al, Adv. Mater. Technol., (2018) 1800013.
“Electrochemical Sensing Based on Printable Temporary Transfer Tattoos”, J. R. Windmiller et al, Chem. Comm. 48 (2012)6794.
“Flexible Rolled Thick-Film Miniaturized Flow-cell for Minimally Invasive Amperometric Sensing”, A. Kagie et al, Electroanalysis, 20, 1610, (2008).
“3-D Printed Artificial Microfish”, W. Zhu, J. Li, et al, Advanced Materials, 27(2015) 4411.
“Thick-Film Textile-based Amperometric Sensors and Biosensors”, M.C. Chuang et al, Analyst, 135(2010)1230.
“Fabrication of Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microfluidic Chips by Atmospheric Molding”, A. Muck et al, Anal. Chem., 76(2004)2290.
“Bulk Modification of Polymeric Microfluidic Devices”, J. Wang, et al, Lab on a Chip, 5(2005)226.
Combinatorial Microneedle Delivery Patch (Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021)
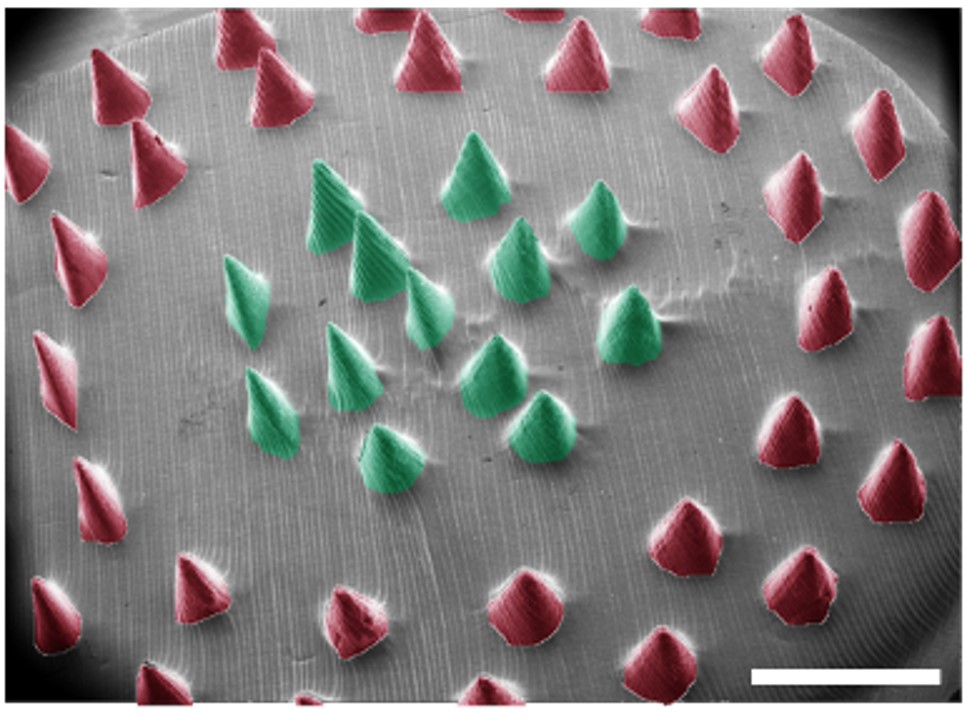
Stretchable & Rechargeable Zn-Ag2O Battery (Advanced Energy Materials, 2017)
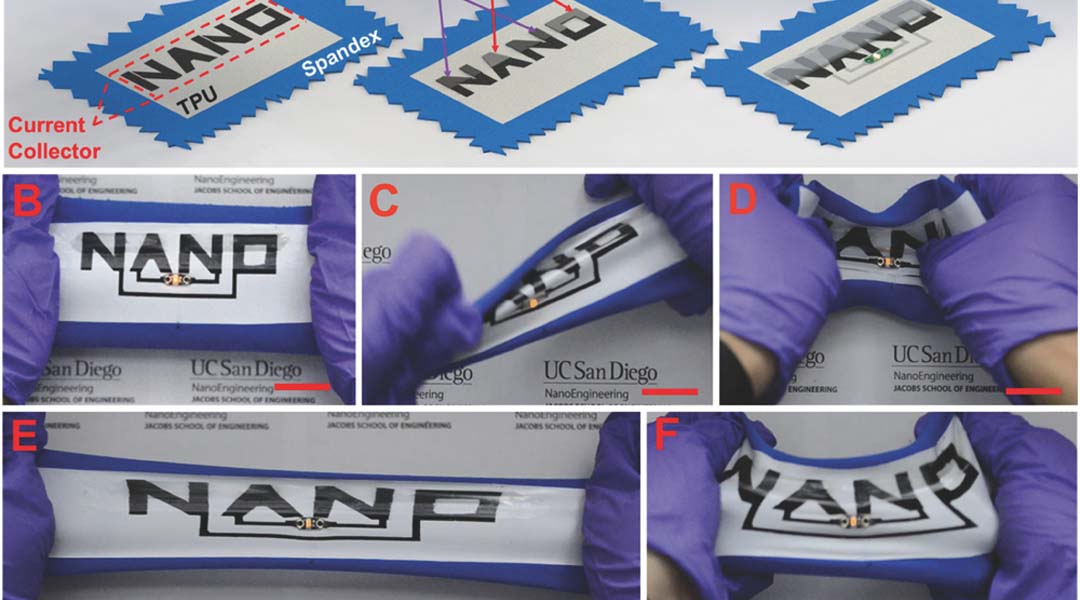

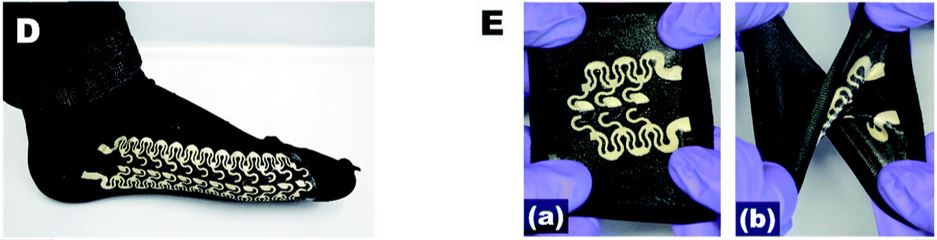
Soft Stretchable “Island–Bridge” Devices (Adv. Mater. Technol., 2017)
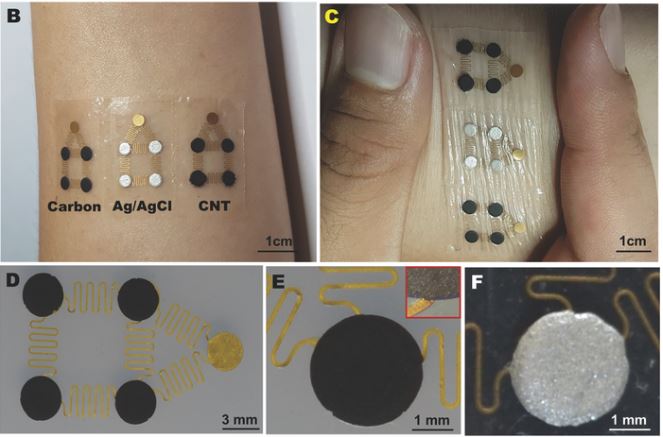
Stretchable biofuel cells (J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016)
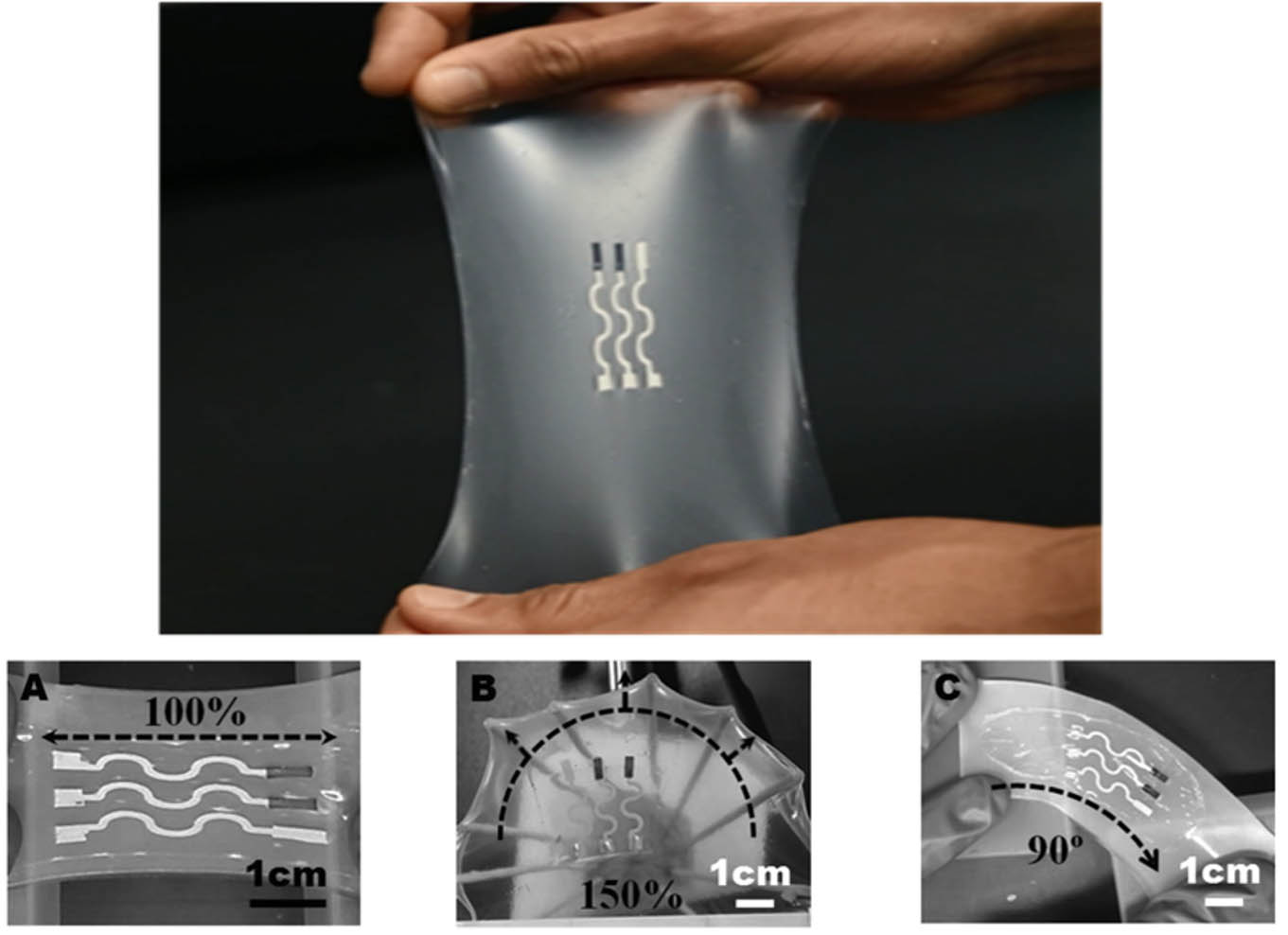
Stretchable printed sensors (Adv. Mater. 2015)
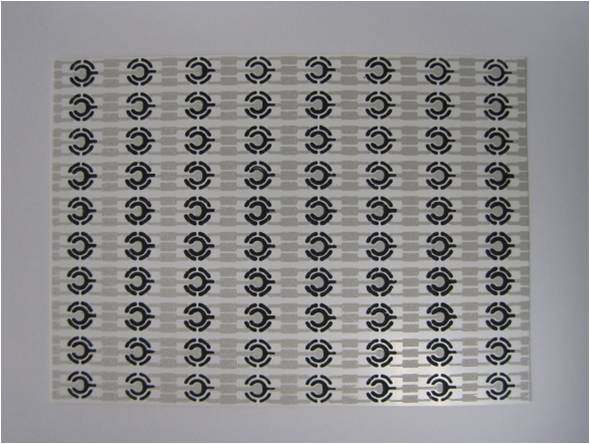
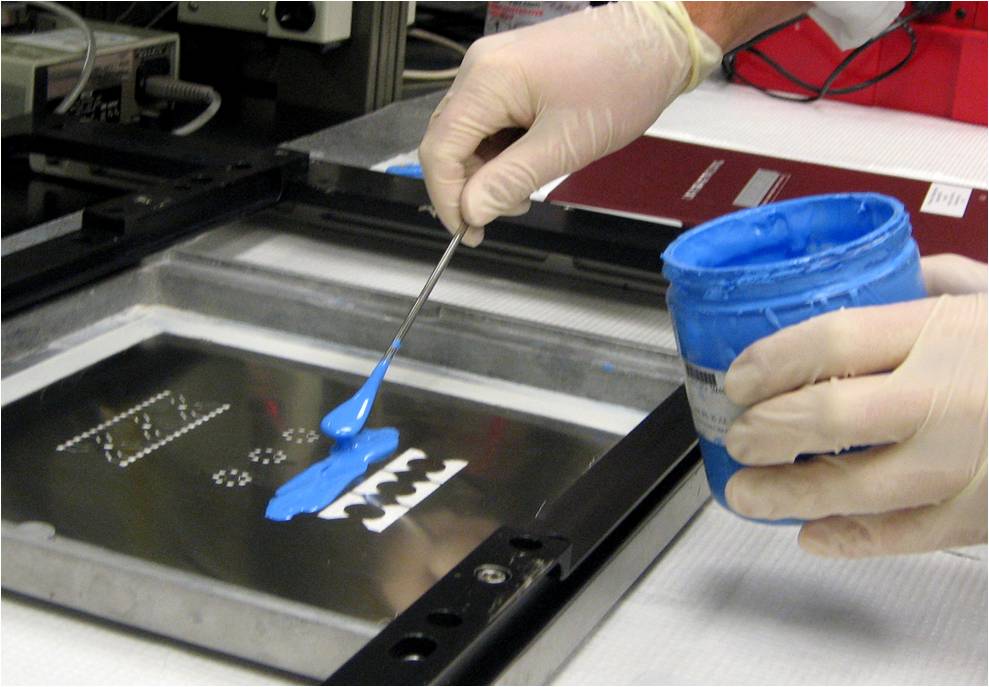
Thick-film fabrication process (Screen-Printing). Mass production of extremely reproducible disposable sensors.
NBE fabricated microneedle for sensing & delivery applications.

Flexible epidermal energy harvesting devices.

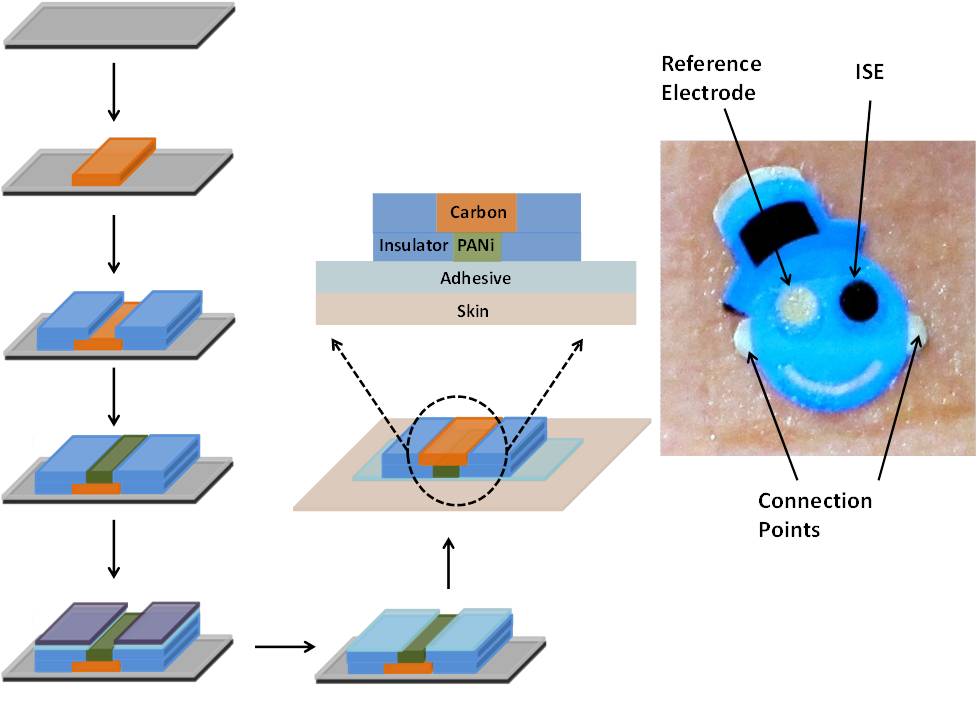
Fabrication protocol employed in the production of temporary transfer tattoo solid-contact ion-selective electrode (ISE) sensors (Analyst 2013)
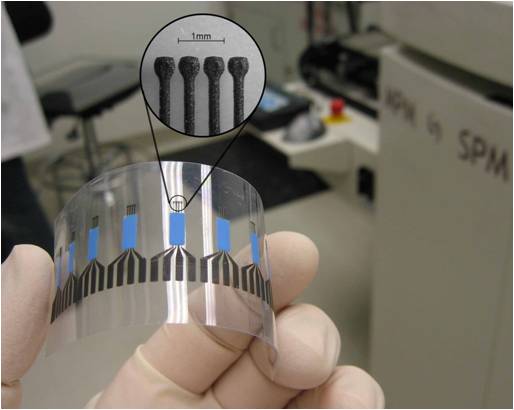
Flexible (Wearable) Printed Sensors
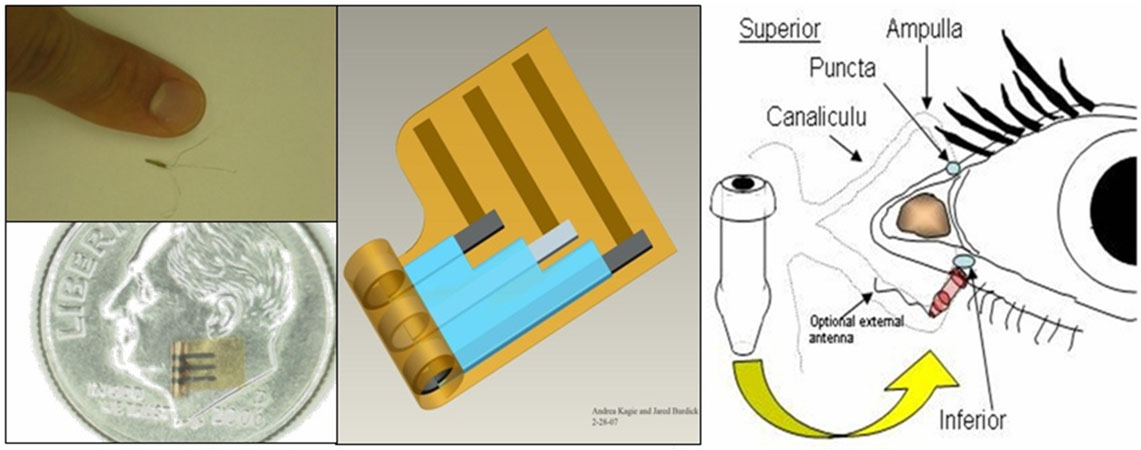
Flexible microfabricated biosensor for glucose monitoring in tears (Electroanalysis 2008).
Preparation of screen printing electrodes.

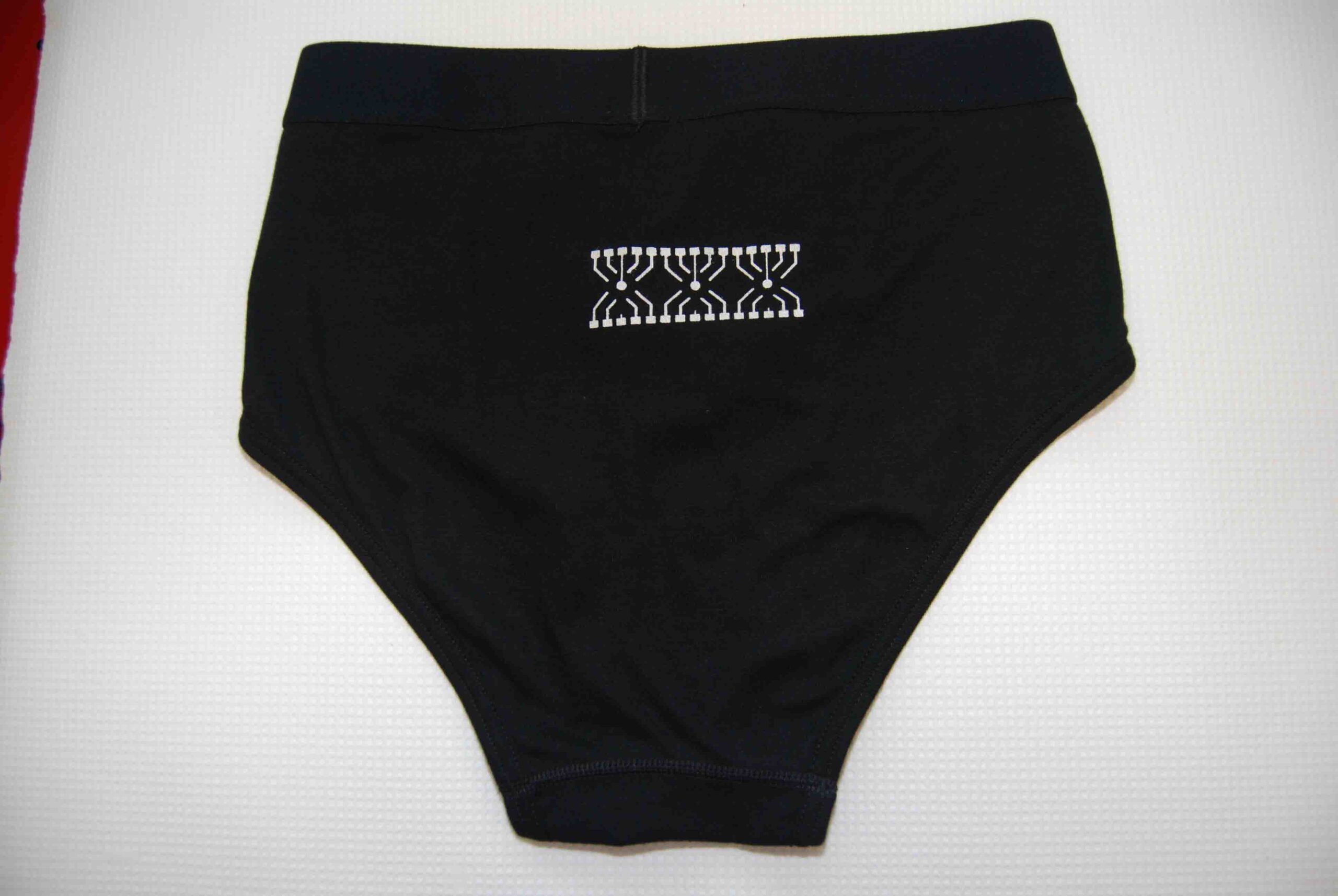
Textile-based thick-film (printable) sensors (‘Smart Underwear”, Analyst, 2010)

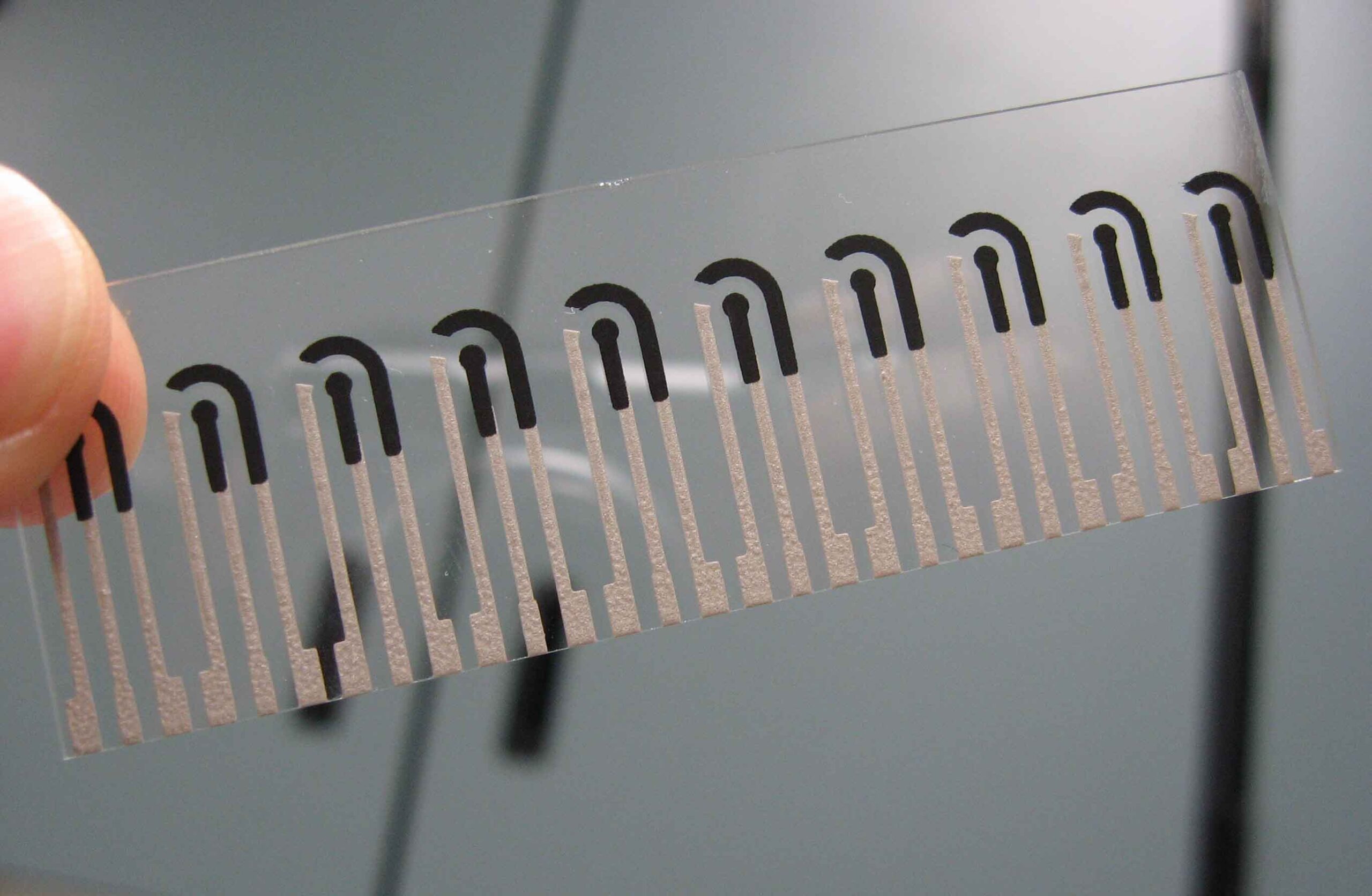
Screen printing electrode on glass slide.
Nanomotor Lithography
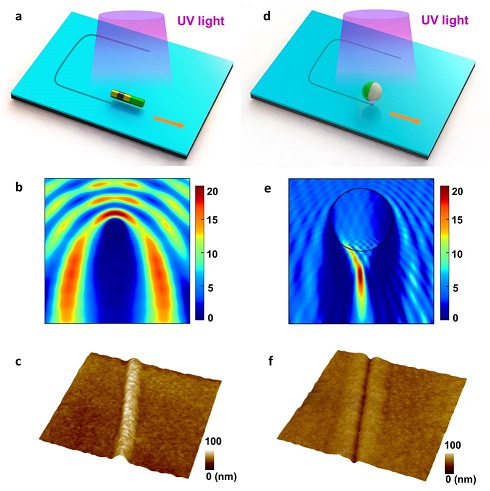
Nanomotor Lithography

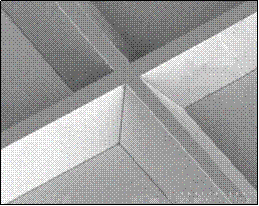
High resolution image of a master used to fabricate microchip || A typical section of a polymer microchip by our group.
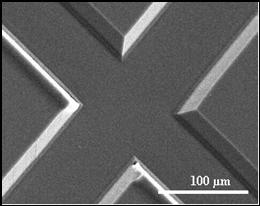
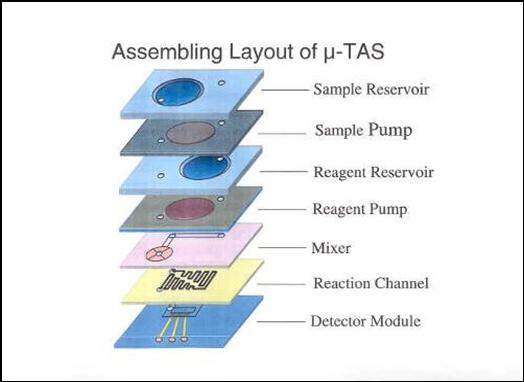
Design of the micro total analysis system
© 2024 Department of Chemcial and Nano Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
